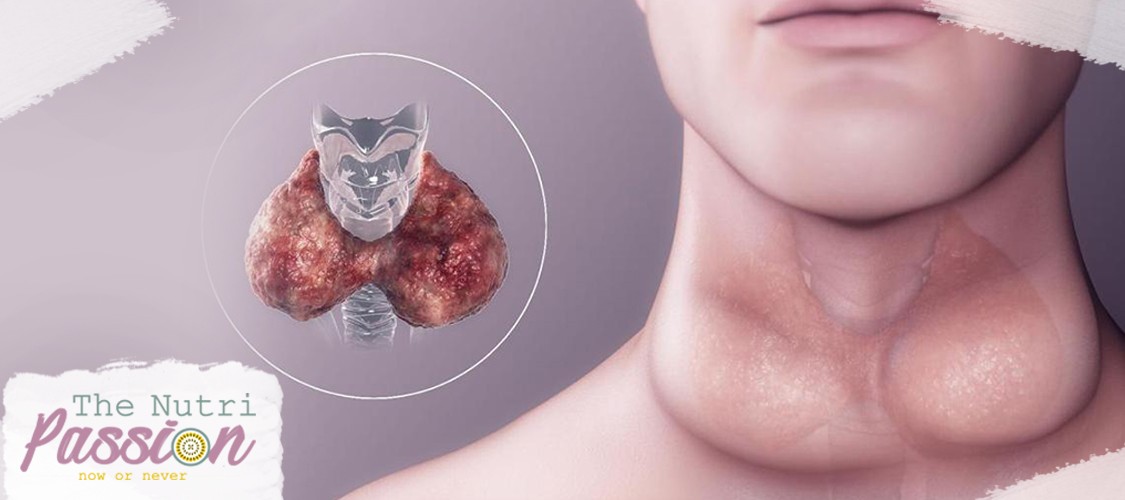
hypothyroidism
What is hypothyroidism?! the thyroid gland produces fewer thyroid hormones than the body needs, in this condition the body's metabolism is negatively affected.
The thyroid gland is a very small gland located in the neck area, and it produces hormones responsible for many vital functions in the body, as these hormones help regulate energy levels in the body, heart rate and many other things.
What are the causes of hypothyroidism?
Autoimmune diseases: immune disorders occur when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the body’s own systems, and this condition is known as Hashimoto’s disease, as this condition is considered a genetic disease
Some medications: Some of the medications that can contribute to hypothyroidism, for example, lithium, which is used to treat certain mental disorders, and iodine-containing drugs, which are used to treat thyroid activity, and cause an opposite reaction, so caution and constant advice should be given when taking any type of medication.
Radiation therapy: which is usually used to fight cancer, especially cervical cancer and lymph nodes.
Thyroid surgery: Removing all or a large part of the thyroid gland will develop hypothyroidism, which requires taking hormone pills for life.
Other causes: such as iodine deficiency, pituitary gland disorder, child birth with hypothyroidism, disorders during or after pregnancy.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism:
These are the main symptoms that may appear on the patient:
• Fatigue.
• Facial swelling.
• Constipation.
• Hair loss and dry skin.
• weight gain.
• Constant pain in joints and muscles.
• Heavy or irregular periods.
• Slowing of the heart rate.
• Inability to tolerate cold.
• Depression.
• Fertility and childbearing problems.
• Loss or decrease in sexual desire.
•numbness in the hands.
•Poor memory
•Enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck area.
Is it possible to have complications?
If the person with hypothyroidism does not follow treatment in time, this may cause the following complications to appear:
• Enlarged thyroid gland, causing difficulty breathing and swallowing.
• Heartbeat problems.
• Neurological and psychological problems.
Myxedema: intolerance to freezing cold, drowsiness accompanied by deep lethargy, and loss of consciousness.
• Complete loss of hearing.
• Anemia.
• Severe thinning of hair on the scalp and eyebrows.
• Hoarseness.
• Enlargement of the heart or its complete failure.
• Infertility.
• Fluid retention around the lungs.
The relationship of hypothyroidism to weight:
As mentioned previously about the effect of the hormones secreted by the thyroid gland on the metabolic rate that responsible for burning calories, therefore, the general weight is affected due to the defect in the secretion of these hormones. It is also related to the severity and degree of inactivity, as the greater the degree of inactivity of the gland, the greater the increase in weight.
Some of the increase in weight is fat, but most of it is a fluid retention inside the body; An underactive thyroid can also affect kidney function, which can increase fluid retention in the body.
Also, the weight gain caused by the inactivity of the thyroid gland is usually not excessive, and is estimated at 2.25-4.5 kilograms; However, some people with hypothyroidism attribute all their excess weight and fat to their wrong eating habits with hypothyroidism.
General advice for thyroid patients:
-Adherence to medication, regular medical examinations, and follow-up with the specialist doctor.
-Moderation in eating is very important, as is calculating the daily calorie needs.
-A lot of vegetables and fruits and the distribution of macronutrients, that is, the elements that the body needs in large quantities in the meal, and that they be integrated in an integrated manner between carbohydrates, fats and protein.
-Commit to moderate and high intensity exercises (aerobic and anaerobic) in order to help improve metabolism for at least an hour 4-5 days a week.
-Enjoy a good sleep at least 6-8 hours a day within the body's biological hours.
-Moderation with coffee and caffeine
-Drinking water
Foods recommended to eat to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body:
-Iodine (eg eggs, cheese, milk and its derivatives, seafood and fish, iodized salt) and in moderation.
- Selenium as it resists cell damage, and maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and its most important sources are chia seeds, mushrooms, tea, meat, rice, oat bran, poultry meat.
-Zinc: Zinc maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and meat, chickpeas, cashews, mushrooms, and pumpkin seeds are among the most important sources of zinc.
-Moderation in eating cruciferous or cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, as well as kale and spinach, as vegetables from this family hinder the thyroid glands use of iodine to manufacture thyroxine
-Gluten-free foods do not have a direct effect on the gland and are not prohibited. However, Celiac patients who are allergic to gluten are an immune disease that may be associated with some immune gland diseases such as Hashimoto. Some may be advised to avoid foods containing gluten.
Other tips to avoid developing hypothyroidism:
-It is important to stay away from foods rich in calories and poor in nutrients necessary for the body.
-It is preferable not to resort to low-calorie and low-carb diets, such as Atkins, keto and other diets.
-The gland patient can follow fasting regimes, taking into account that the fasting hours do not exceed 16 hours, which causes tension in the gland.
hypothyroidism
What is hypothyroidism?! the thyroid gland produces fewer thyroid hormones than the body needs, in this condition the body's metabolism is negatively affected.
The thyroid gland is a very small gland located in the neck area, and it produces hormones responsible for many vital functions in the body, as these hormones help regulate energy levels in the body, heart rate and many other things.
What are the causes of hypothyroidism?
Autoimmune diseases: immune disorders occur when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the body’s own systems, and this condition is known as Hashimoto’s disease, as this condition is considered a genetic disease
Some medications: Some of the medications that can contribute to hypothyroidism, for example, lithium, which is used to treat certain mental disorders, and iodine-containing drugs, which are used to treat thyroid activity, and cause an opposite reaction, so caution and constant advice should be given when taking any type of medication.
Radiation therapy: which is usually used to fight cancer, especially cervical cancer and lymph nodes.
Thyroid surgery: Removing all or a large part of the thyroid gland will develop hypothyroidism, which requires taking hormone pills for life.
Other causes: such as iodine deficiency, pituitary gland disorder, child birth with hypothyroidism, disorders during or after pregnancy.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism:
These are the main symptoms that may appear on the patient:
• Fatigue.
• Facial swelling.
• Constipation.
• Hair loss and dry skin.
• weight gain.
• Constant pain in joints and muscles.
• Heavy or irregular periods.
• Slowing of the heart rate.
• Inability to tolerate cold.
• Depression.
• Fertility and childbearing problems.
• Loss or decrease in sexual desire.
•numbness in the hands.
•Poor memory
•Enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck area.
Is it possible to have complications?
If the person with hypothyroidism does not follow treatment in time, this may cause the following complications to appear:
• Enlarged thyroid gland, causing difficulty breathing and swallowing.
• Heartbeat problems.
• Neurological and psychological problems.
Myxedema: intolerance to freezing cold, drowsiness accompanied by deep lethargy, and loss of consciousness.
• Complete loss of hearing.
• Anemia.
• Severe thinning of hair on the scalp and eyebrows.
• Hoarseness.
• Enlargement of the heart or its complete failure.
• Infertility.
• Fluid retention around the lungs.
The relationship of hypothyroidism to weight:
As mentioned previously about the effect of the hormones secreted by the thyroid gland on the metabolic rate that responsible for burning calories, therefore, the general weight is affected due to the defect in the secretion of these hormones. It is also related to the severity and degree of inactivity, as the greater the degree of inactivity of the gland, the greater the increase in weight.
Some of the increase in weight is fat, but most of it is a fluid retention inside the body; An underactive thyroid can also affect kidney function, which can increase fluid retention in the body.
Also, the weight gain caused by the inactivity of the thyroid gland is usually not excessive, and is estimated at 2.25-4.5 kilograms; However, some people with hypothyroidism attribute all their excess weight and fat to their wrong eating habits with hypothyroidism.
General advice for thyroid patients:
-Adherence to medication, regular medical examinations, and follow-up with the specialist doctor.
-Moderation in eating is very important, as is calculating the daily calorie needs.
-A lot of vegetables and fruits and the distribution of macronutrients, that is, the elements that the body needs in large quantities in the meal, and that they be integrated in an integrated manner between carbohydrates, fats and protein.
-Commit to moderate and high intensity exercises (aerobic and anaerobic) in order to help improve metabolism for at least an hour 4-5 days a week.
-Enjoy a good sleep at least 6-8 hours a day within the body's biological hours.
-Moderation with coffee and caffeine
-Drinking water
Foods recommended to eat to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body:
-Iodine (eg eggs, cheese, milk and its derivatives, seafood and fish, iodized salt) and in moderation.
- Selenium as it resists cell damage, and maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and its most important sources are chia seeds, mushrooms, tea, meat, rice, oat bran, poultry meat.
-Zinc: Zinc maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and meat, chickpeas, cashews, mushrooms, and pumpkin seeds are among the most important sources of zinc.
-Moderation in eating cruciferous or cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, as well as kale and spinach, as vegetables from this family hinder the thyroid glands use of iodine to manufacture thyroxine
-Gluten-free foods do not have a direct effect on the gland and are not prohibited. However, Celiac patients who are allergic to gluten are an immune disease that may be associated with some immune gland diseases such as Hashimoto. Some may be advised to avoid foods containing gluten.
Other tips to avoid developing hypothyroidism:
-It is important to stay away from foods rich in calories and poor in nutrients necessary for the body.
-It is preferable not to resort to low-calorie and low-carb diets, such as Atkins, keto and other diets.
-The gland patient can follow fasting regimes, taking into account that the fasting hours do not exceed 16 hours, which causes tension in the gland.
hypothyroidism
What is hypothyroidism?! the thyroid gland produces fewer thyroid hormones than the body needs, in this condition the body's metabolism is negatively affected.
The thyroid gland is a very small gland located in the neck area, and it produces hormones responsible for many vital functions in the body, as these hormones help regulate energy levels in the body, heart rate and many other things.
What are the causes of hypothyroidism?
Autoimmune diseases: immune disorders occur when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the body’s own systems, and this condition is known as Hashimoto’s disease, as this condition is considered a genetic disease
Some medications: Some of the medications that can contribute to hypothyroidism, for example, lithium, which is used to treat certain mental disorders, and iodine-containing drugs, which are used to treat thyroid activity, and cause an opposite reaction, so caution and constant advice should be given when taking any type of medication.
Radiation therapy: which is usually used to fight cancer, especially cervical cancer and lymph nodes.
Thyroid surgery: Removing all or a large part of the thyroid gland will develop hypothyroidism, which requires taking hormone pills for life.
Other causes: such as iodine deficiency, pituitary gland disorder, child birth with hypothyroidism, disorders during or after pregnancy.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism:
These are the main symptoms that may appear on the patient:
• Fatigue.
• Facial swelling.
• Constipation.
• Hair loss and dry skin.
• weight gain.
• Constant pain in joints and muscles.
• Heavy or irregular periods.
• Slowing of the heart rate.
• Inability to tolerate cold.
• Depression.
• Fertility and childbearing problems.
• Loss or decrease in sexual desire.
•numbness in the hands.
•Poor memory
•Enlargement of the thyroid gland in the neck area.
Is it possible to have complications?
If the person with hypothyroidism does not follow treatment in time, this may cause the following complications to appear:
• Enlarged thyroid gland, causing difficulty breathing and swallowing.
• Heartbeat problems.
• Neurological and psychological problems.
Myxedema: intolerance to freezing cold, drowsiness accompanied by deep lethargy, and loss of consciousness.
• Complete loss of hearing.
• Anemia.
• Severe thinning of hair on the scalp and eyebrows.
• Hoarseness.
• Enlargement of the heart or its complete failure.
• Infertility.
• Fluid retention around the lungs.
The relationship of hypothyroidism to weight:
As mentioned previously about the effect of the hormones secreted by the thyroid gland on the metabolic rate that responsible for burning calories, therefore, the general weight is affected due to the defect in the secretion of these hormones. It is also related to the severity and degree of inactivity, as the greater the degree of inactivity of the gland, the greater the increase in weight.
Some of the increase in weight is fat, but most of it is a fluid retention inside the body; An underactive thyroid can also affect kidney function, which can increase fluid retention in the body.
Also, the weight gain caused by the inactivity of the thyroid gland is usually not excessive, and is estimated at 2.25-4.5 kilograms; However, some people with hypothyroidism attribute all their excess weight and fat to their wrong eating habits with hypothyroidism.
General advice for thyroid patients:
-Adherence to medication, regular medical examinations, and follow-up with the specialist doctor.
-Moderation in eating is very important, as is calculating the daily calorie needs.
-A lot of vegetables and fruits and the distribution of macronutrients, that is, the elements that the body needs in large quantities in the meal, and that they be integrated in an integrated manner between carbohydrates, fats and protein.
-Commit to moderate and high intensity exercises (aerobic and anaerobic) in order to help improve metabolism for at least an hour 4-5 days a week.
-Enjoy a good sleep at least 6-8 hours a day within the body's biological hours.
-Moderation with coffee and caffeine
-Drinking water
Foods recommended to eat to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body:
-Iodine (eg eggs, cheese, milk and its derivatives, seafood and fish, iodized salt) and in moderation.
- Selenium as it resists cell damage, and maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and its most important sources are chia seeds, mushrooms, tea, meat, rice, oat bran, poultry meat.
-Zinc: Zinc maintains the health of the thyroid gland, and meat, chickpeas, cashews, mushrooms, and pumpkin seeds are among the most important sources of zinc.
-Moderation in eating cruciferous or cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, as well as kale and spinach, as vegetables from this family hinder the thyroid glands use of iodine to manufacture thyroxine
-Gluten-free foods do not have a direct effect on the gland and are not prohibited. However, Celiac patients who are allergic to gluten are an immune disease that may be associated with some immune gland diseases such as Hashimoto. Some may be advised to avoid foods containing gluten.
Other tips to avoid developing hypothyroidism:
-It is important to stay away from foods rich in calories and poor in nutrients necessary for the body.
-It is preferable not to resort to low-calorie and low-carb diets, such as Atkins, keto and other diets.
-The gland patient can follow fasting regimes, taking into account that the fasting hours do not exceed 16 hours, which causes tension in the gland.

Post Comment